Theories of Child Development
As an expert in theories of child development, I delve into various theories that shed light on the intricate process of how children grow, learn, and mature. Understanding these theories is crucial for parents, educators, and caregivers to provide optimal environments for children to thrive. From classical theorists like Freud and Erikson to contemporary researchers such as Piaget and Vygotsky, each theory offers unique insights into different aspects of child development.
Exploring the foundations of child development theories of child development reveals a rich tapestry of ideas that have shaped our understanding of how children form attachments, acquire language skills, develop cognitive abilities, and navigate social interactions. By examining the core principles of these theories, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities involved in nurturing young minds and supporting their growth.
Through this article, I aim to demystify key concepts within various theories of child development and highlight their practical implications for those involved in caring for children. By synthesizing research-based knowledge with real-world examples, I hope to empower readers with valuable insights that can inform their interactions with children and enhance their ability to foster healthy development across different domains.
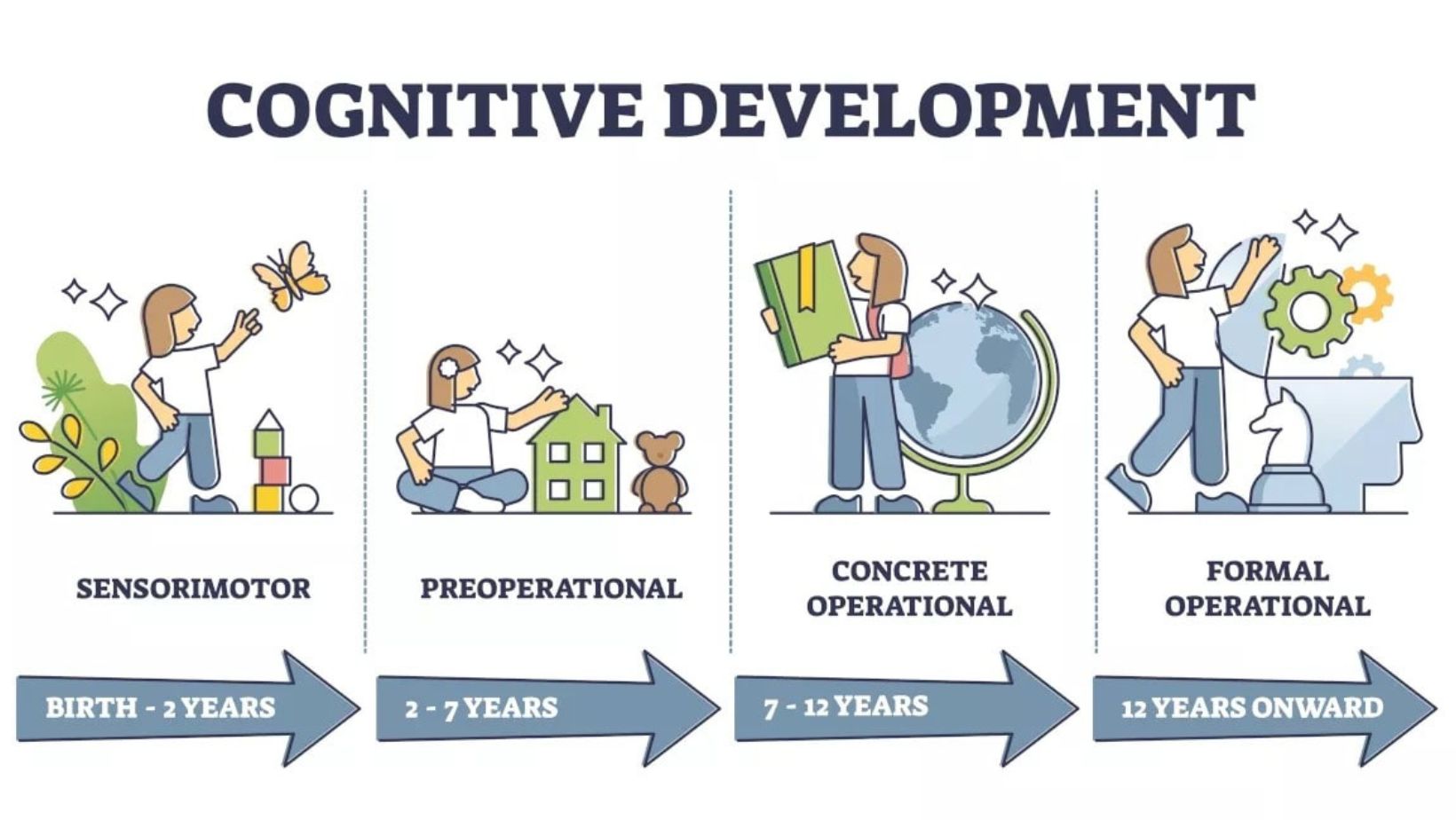
Psychoanalytic Theory
When delving into theories of child development, Psychoanalytic Theory offers a unique perspective on how individuals evolve emotionally and psychologically during their formative years. This theory, pioneered by Sigmund Freud, focuses on the unconscious mind’s impact on behavior and personality development in children.
One key concept within Psychoanalytic Theory is the division of the human psyche into three parts: the id, ego, and superego. The id represents primal instincts and desires, seeking immediate gratification. In contrast, the ego acts as a mediator between the id’s impulses and external reality. Finally, the superego develops through social interactions and internalizes societal norms and values.
Freud also introduced stages of psychosexual development that play a crucial role in shaping a child’s personality. These stages include oral, anal, phallic, latent, and genital stages. Each stage presents unique challenges that must be resolved for healthy psychological development to occur.
An important aspect of Psychoanalytic Theory is its emphasis on early childhood experiences’ lasting impact on an individual’s life. Traumatic events or unresolved conflicts during childhood can manifest in adulthood through various behaviors or mental health issues.
As we explore further into this theory throughout this article on child development theories, it becomes apparent how Freud’s groundbreaking ideas laid the foundation for understanding complex human behaviors from a developmental perspective.
Behaviorism Theory
When delving into the realm of child development, one prominent theory to explore is Behaviorism. Developed by renowned psychologists such as John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner, Behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors rather than internal mental processes.
In this theory, it’s believed that children learn through a process of association and reinforcement. For instance, if a child receives praise for completing a task, they are more likely to repeat that behavior in the future. Conversely, if a behavior leads to a negative outcome, the child may be less inclined to engage in it again.
Key Principles of Behaviorism Theory:
- Stimulus-Response: Children react to stimuli in their environment with certain responses.
- Operant Conditioning: Behaviors are shaped by consequences like rewards or punishments.
- Observational Learning: Children can also learn by observing others and mimicking their actions.
By applying these principles in practice, parents and educators can effectively shape children’s behaviors and encourage positive development. Through consistent reinforcement of desired behaviors and clear consequences for negative ones, adults play a crucial role in guiding children towards healthy growth and learning experiences.
Behaviorism theory provides valuable insights into how external factors influence child development. By understanding how behaviors are learned and reinforced, we can create environments that support children’s cognitive, emotional, and social development effectively.

